Related items loading ...
Section 1: Publication
Publication Type
Journal Article
Authorship
Richardson, M., Kumar, P., Sonnentag, O., and Marsh, P.
Title
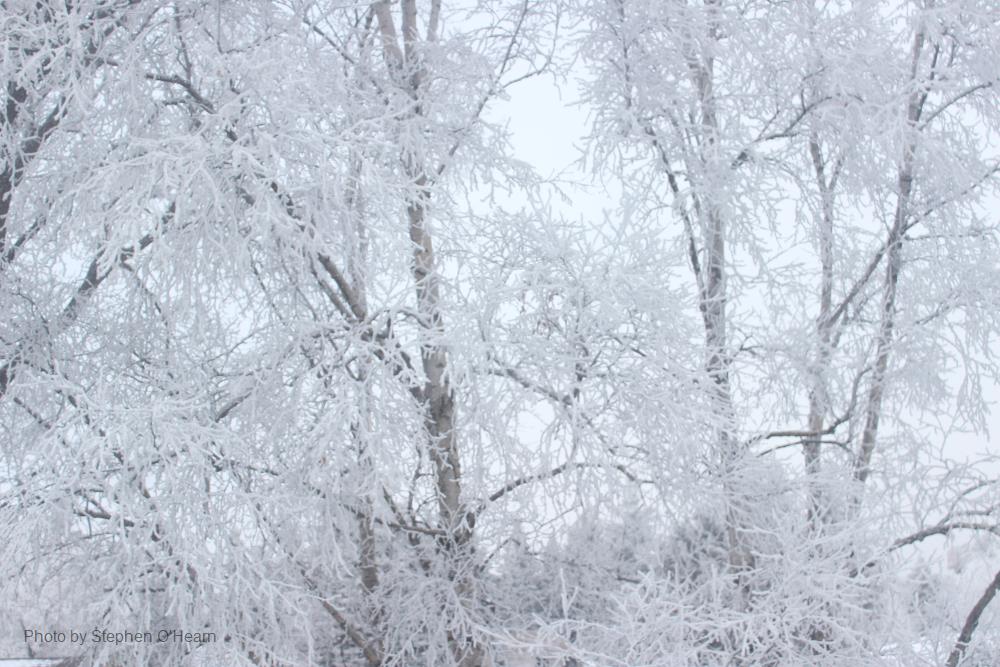
Thermodynamic basis for the demarcation of Arctic and alpine treelines
Year
2022
Publication Outlet
Scientific Reports, In review
DOI
ISBN
ISSN
Citation
Richardson, M., Kumar, P., Sonnentag, O., and Marsh, P.: Thermodynamic basis for the demarcation of Arctic and alpine treelines, Scientific Reports, In review
Abstract
At the edge of alpine and Arctic ecosystems all over the world, a transition zone exists beyond which it is either infeasible or unfavorable for trees to exist, colloquially identified as the treeline. We explore the possibility of a thermodynamic basis behind this demarcation in vegetation by considering ecosystems as open systems driven by thermodynamic advantage—defined by vegetation’s ability to dissipate heat from the earth’s surface to the air above the canopy. To deduce whether forests would be more thermodynamically advantageous than existing ecosystems beyond treelines, we construct and examine counterfactual scenarios in which trees exist beyond a treeline instead of the existing alpine meadow or Arctic tundra. Meteorological data from the Italian Alps, United States Rocky Mountains, and Western Canadian Taiga-Tundra are used as forcing for model computation of ecosystem work and temperature gradients at sites on both sides of each treeline with and without trees. Model results indicate that the alpine sites do not support trees beyond the treeline, as their presence would result in excessive CO2 loss and extended periods of snowpack due to temperature inversions (i.e., positive temperature gradient from the earth surface to the atmosphere). Further, both Arctic and alpine sites exhibit negative work resulting in positive feedback between vegetation heat dissipation and temperature gradient, thereby extending the duration of temperature inversions. These conditions demonstrate thermodynamic infeasibility associated with the counterfactual scenario of trees existing beyond a treeline. Thus, we conclude that, in addition to resource constraints, a treeline is an outcome of an ecosystem’s ability to self-organize towards the most advantageous vegetation structure facilitated by thermodynamic feasibility.
Plain Language Summary
Section 2: Additional Information
Program Affiliations
Project Affiliations
Submitters
Publication Stage
Published
Theme
Presentation Format
Additional Information
Northern-Water-Futures, Refereed Publications


 GWFNet
GWFNet Master
Master Data
Data Research
Research Map
Map
 Advanced
Advanced Tools
Tools
 . . .
. . .
 Metadata Editor
Metadata Editor
 Record List
Record List
 Alias List Editor
Alias List Editor
 Legacy sites
Legacy sites